Research Methods in Health Sciences
Course Number: HE201
Subject: Health Sciences
Literature Review
A literature review is a survey of research about a particular topic.
- It's specific - focuses on a well-defined research question.
- It's selective - includes a curated selection of research.
- It's a synthesis - brings together discussions from across the research.
- It's a starting point - identifies where your research fits into the picture.
- It shows accountability - demonstrates how you're tuning-in to others' work and voices responsibly.
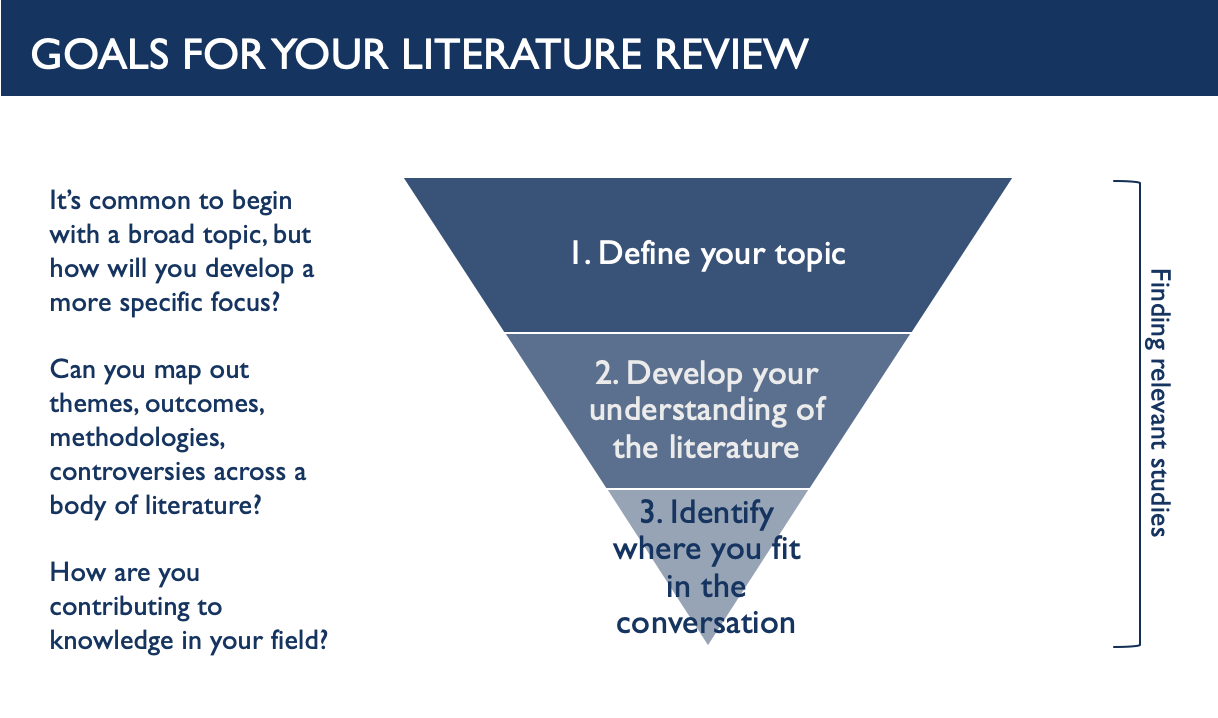
Image description
Goals for your literature review. 1. Define your topic. It’s common to begin with a broad topic, but how will you develop a more specific focus? 2. Develop your understanding of the literature. Can you map out a themes, outcomes, methodologies, controversies across a body of literature? 3. Identify where you fit in the conversation. How are you contributing to knowledge in your field? Throughout all 3 stages, you'll be finding relevant studies.
Topic Development
Learning About Your Topic
- Before developing a research question, it's helpful to learn a bit about your topic.
- Both Omni and Google Scholar can be useful for this kind of preliminary searching.
- Try to find out what questions researchers are asking about your topic, what terms they use to talk about the topic, and any key journals they publish in.
- From your search results, read only the article titles and abstracts of titles that sound interesting.
Research Question
- A well-defined research question gives direction to your searching.
- Frameworks can give guidance about what to include.
PICO (for clinical topics)
Patient, population, or problem - Who is my question about?
Intervention - What is the intervention?
Comparison - Is there a comparison intervention?
Outcome - What is the outcome?
EDP(T)
Exposure - Could include socioeconomic status, health-related behaviours, health status or environmental exposures.
Disease - What disease, disorder or injury am I interested in?
Population - Who is my question about?
Time - What time period is relevant?
Building a Search
Search Terms
Keywords
What are the major concepts in your topic? What are some synonyms or alternate terms you can use?
- Consider the terms typically used in research literature.
- Google "synonyms for ..."
- If you have an on-topic article, see what terms get used in the title/abstract.
Major Concept | Keywords |
|---|---|
Cancer | cancer, neoplasm, melanoma |
Article Databases
There is a list of databases relevant to Health Sciences. Choose databases to search based on the descriptions.
- Limit results to peer-reviewed.
- Sort by most recent publications first.
- Discover key articles.
- Recognize key scholars.
- Avoid missing important results.
- Cut out irrelevant results.
Search Tactics
Try using some of the following database search tactics to get better results.
What is the tactic? | What does the tactic do? | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Boolean AND | Use AND to ensure that all terms appear in every search result. | depression AND home care |
Boolean OR | Use OR to ensure that at least one term appears in every search result. | transgender OR GBTQ OR GLBT |
Phrase searching | Use “quotation marks” to find more than one term in a row. | “brain cancer” |
Truncation | Use an asterisk* at the end of a term to include multiple endings. | trauma* trauma, traumatic, traumatically, raumatize, traumatized, traumatizing |
Wildcard | Use a question mark ? within a term to search for variations of a single character. | decoloni?e decolonize, decolonise |
Question! I did a search for cancer AND music therapy in CINAHL.
- What happens to the # of results if I search for cancer AND "music therapy"?
- What happens to the # of results if I search for cancer* AND "music therapy"?
Field Searching
- Use the drop-down beside a search box to find terms in specific areas of results. Codes beside each field tell the database where to search for a term.
Example: ti("adverse childhood experiences") in PsycINFO (all results will have the term in titles).
Limits
- You can limit results to peer-reviewed or scholarly.
- A date limit is also often useful in health research.
Subjects
- These are controlled terms from a database thesaurus that are assigned to articles.
- Databases have different thesauri, which affects the subjects you use.
- Note: you'll usually see a link to the "Subjects Headings" or thesaurus in a database's menu.
Example: MESH.EXACT("Health Services for Transgender Persons") in MEDLINE (ProQuest)
Example: (MH "Transgender Persons+") in CINAHL
Major Concept | Keywords | Subjects |
|---|---|---|
Cancer | cancer, neoplasm, melanoma | CINAHL: Neoplasms Melanoma |
Question! What is the CINAHL subject for teenager?
Search Strategy Planning Worksheet
Managing Relevant Results
Citation management software = a method for storing, organizing, and citing literature you can use as you search.
